
Spyrometry
What is spirometry?
Spirometry is the most common test for measuring lung function and respiratory efficiency. Respiratory function tests are based on various examinations ranging from measuring respiratory flow volumes (Figure 1) to estimate the “physical characteristics” that underlie blood gas exchange. The analysis of the results of the test performed through the spirometer, integrated with the patient’s clinical history, allows to understand and study in-depth the respiratory system for the diagnosis of the disease and its therapy.
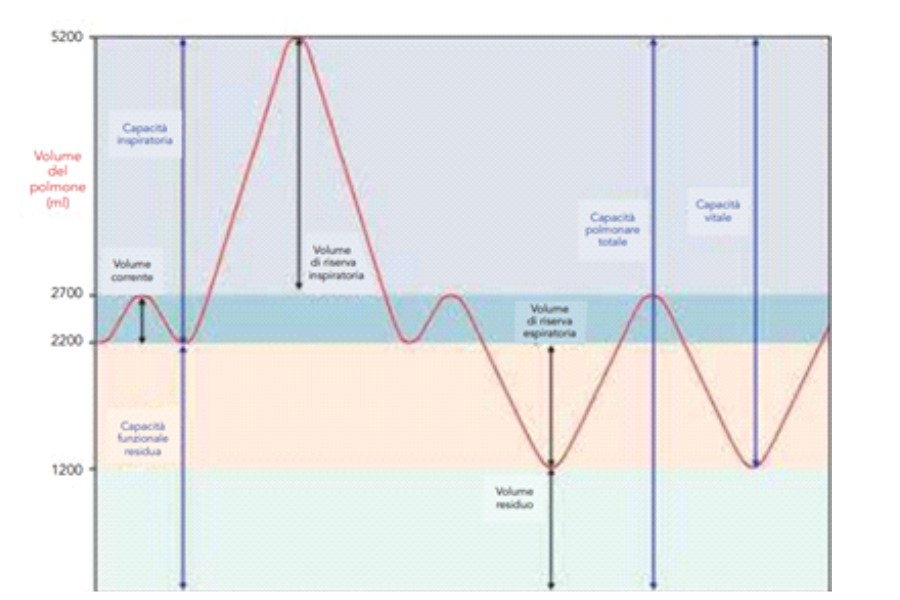
Figura 1 Grafico dei volumi respiratori
Simple and Global Spirometry
Standard spirometry is the so-called simple spirometry and has as its diagnostic objective is to detect obstructive pathologies such as asthma and COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease). Global spirometry aims to study less common pathologies of restrictive origin characterized by the insufficient capacity of the thoracopulmonary system to mobilize air volumes adequately.
How is spirometry done?
To perform spirometry, the patient must breathe into a cardboard mouthpiece connected to the spirometer. Breathing through the mouth only is required, and a nose clip is used to prevent breathing through the nose.
Once the test begins, the spirometer measures the results of slow breathing and forced breathing. In slow breathing, the subject usually breathes. In forced breathing, the issue is asked to inhale to the maximum total lung capacity (TPC) followed by a maximum exhale (RV), in which all accumulated air is expelled.
Why is spirometry important for pulmonary rehabilitation?
Spirometry, in addition to the diagnosis, allows the monitoring and evaluation of drug therapy as well as representing an essential means for the assessment of the entire individual rehabilitation project of the patient, aimed at its clinical stabilization, the reduction of disability resulting from the disease, improving the quality of life and increasing survival.
Spirometry in the pandemic era
In Italy, during the COVID-19 pandemic peak phase, respiratory pathophysiology laboratories postponed all non-urgent, preventive, and routine pulmonary function tests, limiting themselves to performing only necessary tests. Thus, there was a substantial reduction of 19% in asthma diagnoses and an apparent reduction in spirometry tests (-45%), resulting in fewer diagnoses of obstructive diseases.
Following this substantial decrease, we can ask ourselves what will impact our health and economic and health terms. An important aspect to be taken into account to define the degree of restrictions/precautions adopted during the pandemic period in the performance of respiratory tests is the potential spread of SARS-CoV-2, as pulmonary function tests can be included among the procedures that generate aerosols, causing a possible increase in the risk of transmission between subjects and health personnel.
Eurospiro line, LUMED accessories for spirometry
Eurospiro is the line of accessories for ergospirometry and metabolic tests offered by LUMED, in particular:
Individually packed is practical and hygienic. Made from quality Kraft paper, it comes in boxes or dispensers.
The viral, antibacterial filter is highly reliable and provides a high degree of protection for both the patient and the spirometer. In addition, its low resistance allows for accurate results.
Made of hypoallergenic material and rubber or foam pads to perfect fit and improve patient comfort.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
- “Global spirometry, survey for evaluation of respiratory function” Author Prof. Carlo Mereu., 2016
- World Asthma Day. Closed outpatient clinics drop in diagnoses. Press Office AIPO-ITS., May 2021
- Respiratory function testing in the era of the covid-19 pandemic AIPO-ITS Position Paper., May 2020





